WhatsApp: +8619037303916
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +8619037303916
Email: [email protected]
Nowadays, in our lives, motors are almost everywhere, from aerospace, ships, cars to washing machines, fans, vacuum cleaners, electric robots, etc. in our lives.
Motors are used in almost all application scenarios, and the drive device controls them. But almost different types of motors have different running times. Some motors are always in operation, and some motors run for a short period of time during the work cycle or alternately run during the cycle. Therefore, based on this, the concept of motor duty system was introduced.
The motor duty actually refers to the working state of the motor, such as continuous operation or short-term operation or intermittent operation.
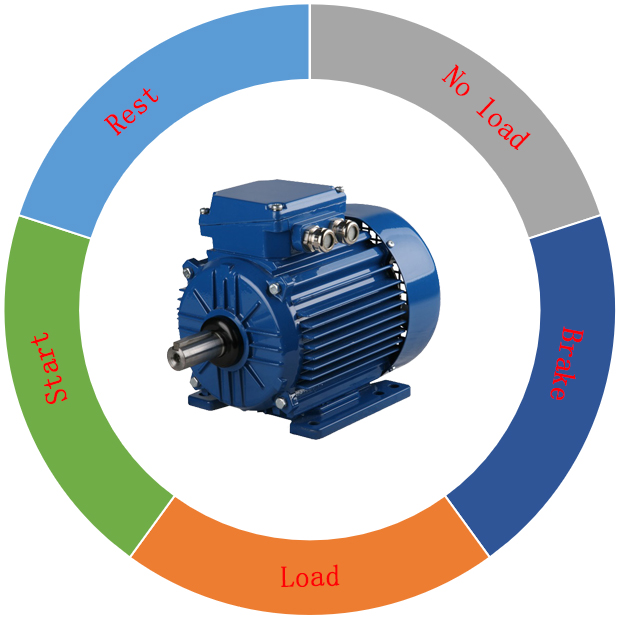
In order to understand the working system of the motor more intuitively, we can divide the working cycle of the motor into time periods such as start, load, brake, no-load, and rest, as well as the duration and sequence of the phases. (Including start, load, brake, no load)
1.Types of working duty
The working duty of the motor can be roughly divided into 3 categories according to the length of the working time of the motor:
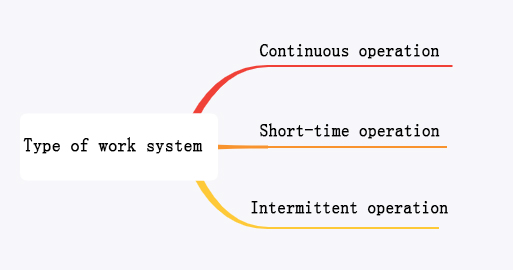
1.1 The continuous working duty means that the motor can run continuously under the rated voltage and rated load without stopping the operation. When the user does not indicate the working duty, the manufacturer shall consider it to be a continuous working system.
1.2 Periodic working duty means that the motor can only run intermittently under rated conditions, that is, the motor needs to "rest" after working for a period of time. It is usually expressed by the duty cycle, that is, in a cycle, the percentage of the ratio of the motor's continuous load operation time to the cycle. There are generally four types: 15%, 25%, 40% and 60%.
For example, a motor running at a temporary load rate of 40% will work for 4 minutes and 6 minutes of "rest" in a 10-minute cycle, and it will run alternately in this way. If the motor's operation exceeds the duty cycle, it may be overloaded and damaged.
1.3 The short-time work duty means that the motor can only run within a limited time under rated conditions, with a short working period and a long stop period. When the motor has been running under the rated load for the specified time, it must be stopped and restarted only after it has cooled down.
If it continues to run beyond the specified time, the motor may overheat and be damaged. There are four standards for the duration of short-term motor operation: 10/30/60/90min.
2. Division of work duty
In IEC60034-1, 10 types of motor work duty are divided and characterized. Each type of work duty has relevant instructions for the load conditions of the motor, including start-up, electric brake, no-load, power-off stall, and phased Duration and sequence.
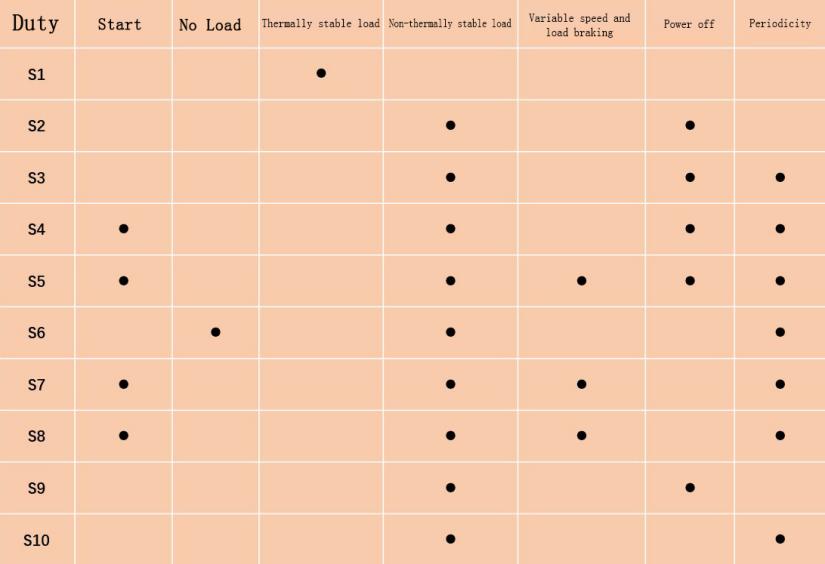
EC60034 is one of the most important standards in all motor standards, corresponding to the Chinese standard GBT755.
S1 continuous work duty
The running time under constant load is sufficient to achieve thermal stability, and it will be thermally stable even if it runs continuously, so there are no parameters that need to be reached.
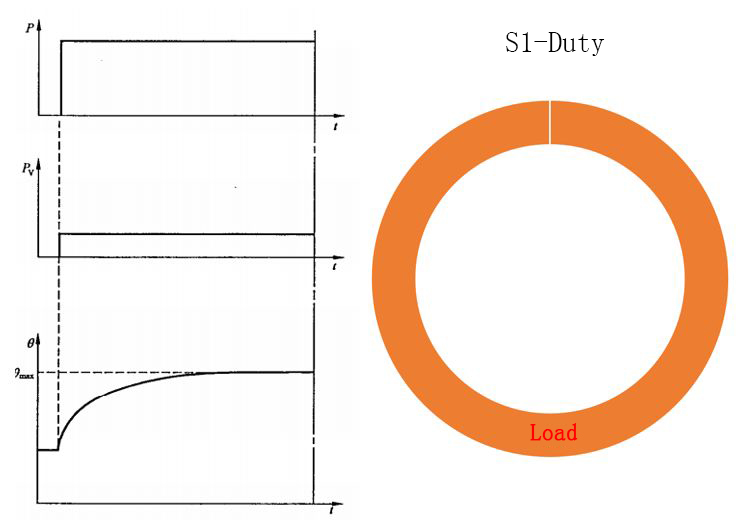
This work duty shows that the motor can run for a long enough time and the temperature reaches a stable value. The S1 work system motor is often used to control drives, compressors, conveyors, etc. in factories.
S2 short-time work duty
Running for a given time under constant load, this time is not enough to reach thermal stability, and then the energy is cut off for a long enough time, so that the motor is cooled again to within 2K of the temperature of the cooling medium.
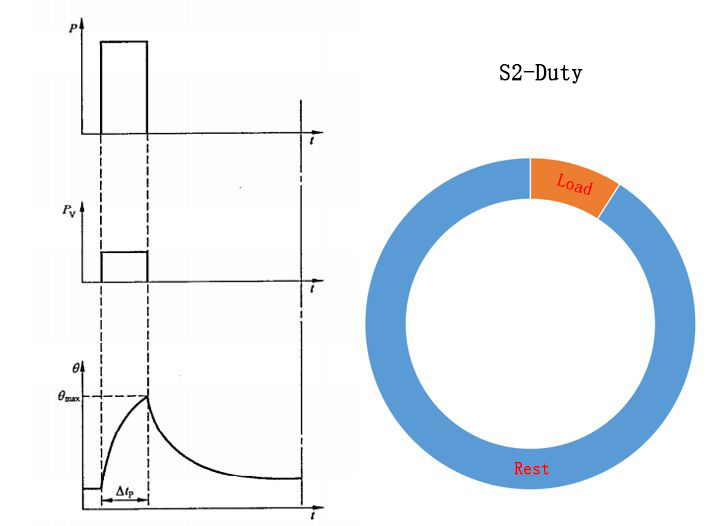
In this working duty, the motor running time is very short, and the heating time is much lower than the cooling time. Therefore, the motor will be preheated to ambient temperature before running again. Motors of this kind of working system are commonly found in cranes, household appliances drives, valve controllers, and so on.
S3 intermittent work duty
Run according to a series of the same work cycle that does not reach the thermal equilibrium state, each cycle includes a period of constant load operation time and a period of shutdown interval (energy-off stop time). The load duration is the ratio of the constant load operating time to the load cycle.
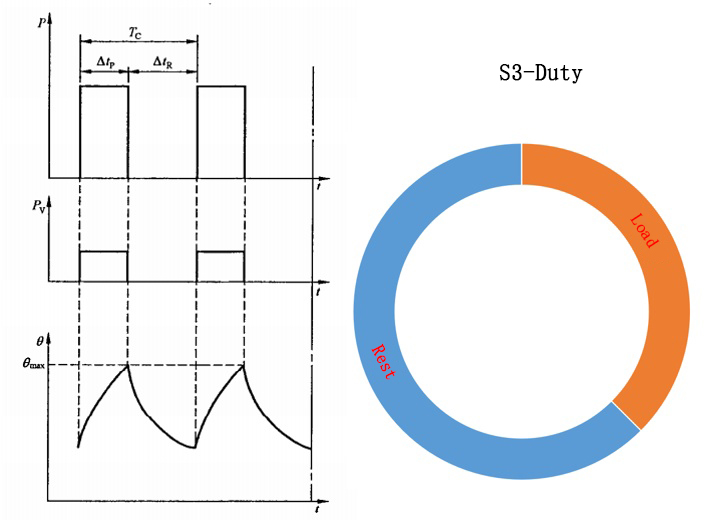
The starting current of each cycle in this working duty has no significant effect on the temperature rise. However, the cycle must last for 10 minutes, and the temporary load rate must be one of 15%, 25%, 40%, and 60%. Motors of this type of work are commonly used on punching and drilling machines.
S4 includes intermittent cycle work duty for starting
Run according to a series of the same work cycle, each cycle includes a period of starting time that has a significant impact on temperature rise, a period of constant load operation time, and a period of power-off and shutdown time.
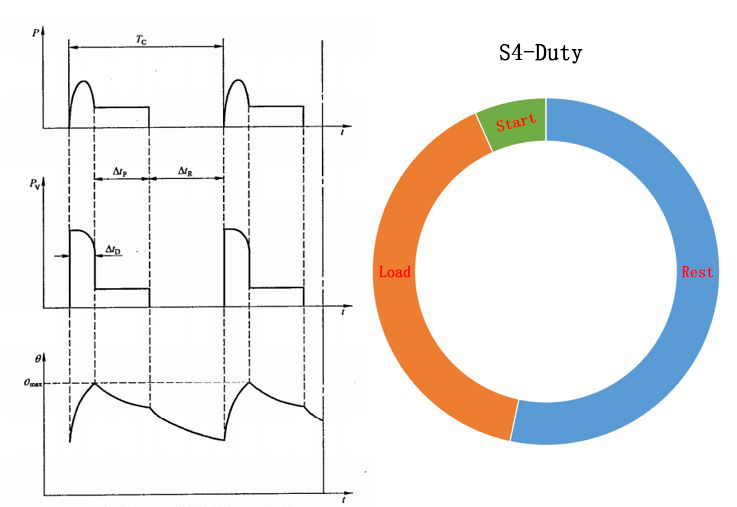
Similar to S3, but start is added on the basis of S3, so the moment of inertia of the motor load is required, that is, the acceleration capability of the motor. The motors of this working duty are widely used in metal cutting machines, drilling machines, mine hoists, etc.
S5 Intermittent duty cycle including electric braking
Run according to a series of the same working cycle, each cycle includes a period of starting time, a period of constant load operation time, a period of fast electric braking time and a period of power-off stopping time.
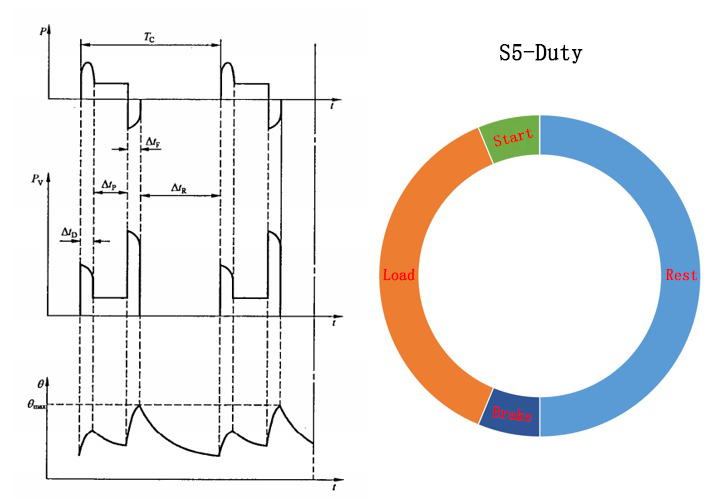
Similar to S4, the moment of inertia of the motor load is required. However, all time periods are too short to reach their respective steady-state temperatures. This working duty motor is commonly used in billet rolling mills, manipulator drives, mine hoists, etc.
S6 continuous cycle work duty
Run according to a series of the same work cycle, each cycle includes a period of constant load operation time and a period of no-load operation time, but does not stop.
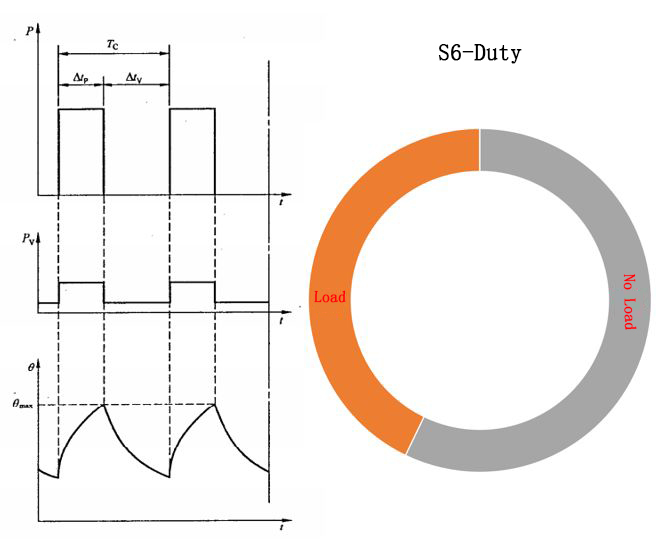
Operating cycle = work (load + no load), refer to S3. Commonly used in presses, cutting machines, etc.
S7 includes the continuous cycle work duty of electric brake
Run according to a series of the same working cycle, each cycle includes a period of starting time, a period of constant load operation time and a period of fast electric braking time, without stopping. That is, S6 for starting has been added. Mainly used in ginning machine.
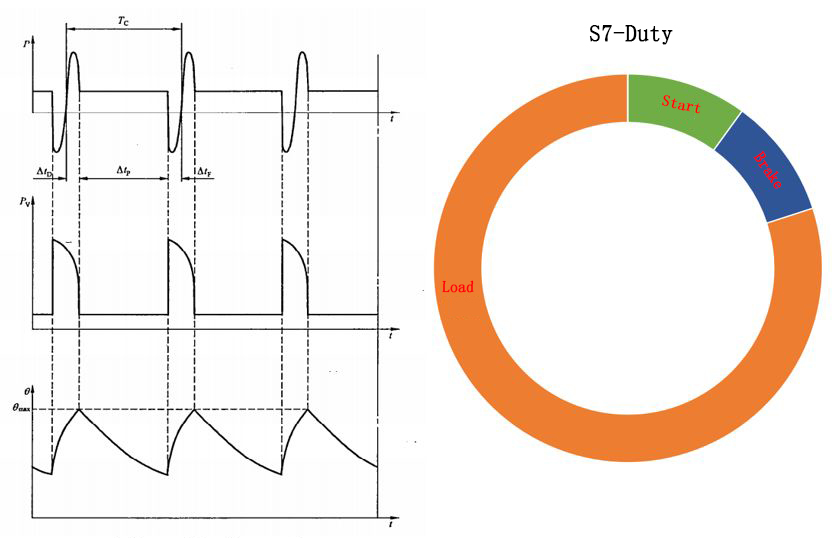
S8 includes a continuous cycle working duty with variable speed and variable load
It is more complicated. In this kind of work system, the motor is operated by a series of identical work cycles that have not reached the thermal equilibrium state.
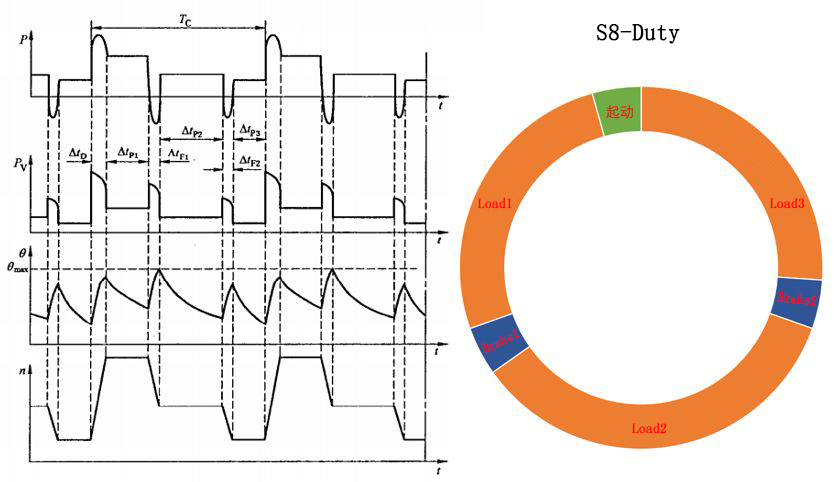
Each cycle includes a period of constant load running time at a predetermined speed, and one or more periods of other constant load running time at different speeds. There is no rest time, and it runs all the time, but all of the time is very short and cannot reach the steady state temperature.
S9 load and speed non-periodic change working duty
Non-periodical work duty in which the load and speed change within the allowable range. This kind of work duty includes frequent overload, and its value can exceed full load. It is more complicated, and is often regulated according to actual conditions, such as wind power generation.
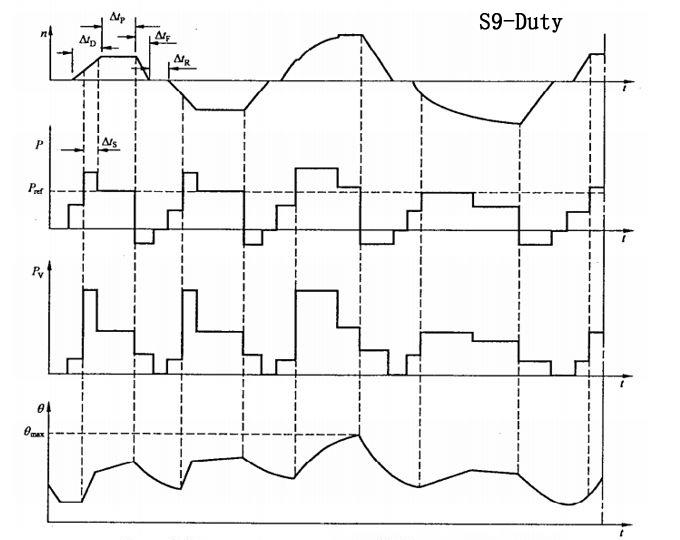
S10 Discrete Constant Load Work duty
Including no less than 4 kinds of discrete load values (or equivalent load) of the work duty, which can include no-load operation and shutdown, under each load, reach the thermal equilibrium state (even no-load or shutdown), in a work the minimum load value in the cycle can be zero. Compared with S8, it can be considered that there are a lot of constant load motions, which require various loads and time, but do not include acceleration and deceleration.
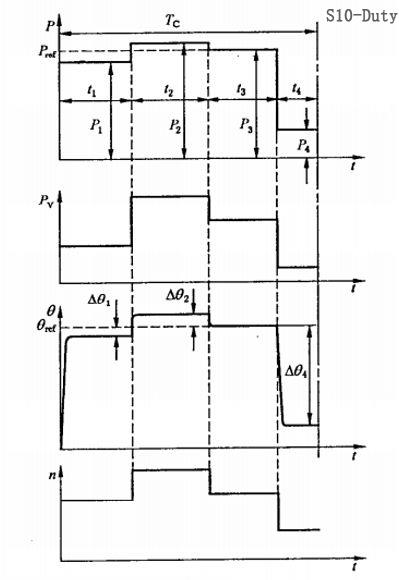
The motor work duty refers to the specific method of controlling the movement of the motor. It is a kind of work instruction to avoid the motor from overheating and burning out. It is also a kind of user demand. At the same time, it also guides you to choose a suitable motor according to the working duty of the motor. However, in practical applications, the working duty of many motors are diversified, and one or more working duty are required at the same time to meet different application scenarios.
TO TOP